As you probably know from our recent news, Online Domain Tools allows you to create so called Runlinks and Permalinks. What are these good for and how to use them is the topic of this post. We will uncover some technical details so that you are able to get most of these new features.
What Is Runlink?
Runlink is a link that specifies a tool you want to run and how to run it – i.e. the tool’s arguments. A Runlink can be created either manually or using a Runlink button, which is easier and preferred method. Let’s have a look at a simple example. We will create a Runlink for Ping Online that is going to send 2 pings to google.com with 5 second timeouts and other Ping Online arguments will be left with their default values.
- We type http://ping.online-domain-tools.com/ to the browser’s address bar.
- We fill the desired arguments in the input form as if we wanted to run the tool with these arguments.
- Click the Runlink button on the right below the input form.
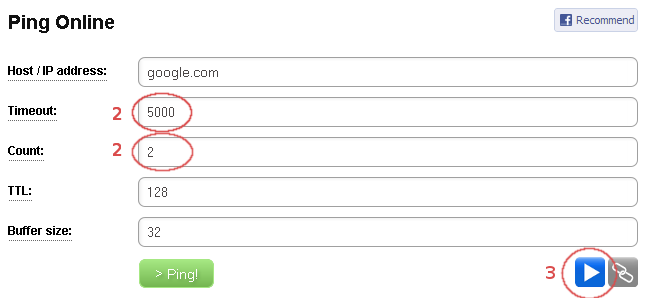
- A window with the link pops up.
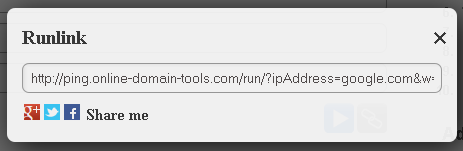
- The generated link looks as follows:
http://ping.online-domain-tools.com/run/?ipAddress=google.com&w=5000&n=2&i=128&l=32
As we can see, “run/” was appended to the path of Ping Online’s URL. This tells the server that it is a Runlink. Then we can see the query string contains all the arguments from the input for
- ipAddress contains the value of the Host / IP address field;
- w contains the value of the Timeout field;
- n contains the value of the Count field;
- i contains the value of the TTL field;
- l contains the value of the Buffer size field.
- Now we can copy the given link into the address bar of our browser and see what happens. It is not a big surprise that we have just executed Ping Online with the given arguments.
